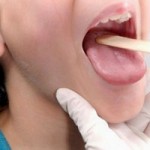
Acute inflammation of the throat or pharyngitis can be related to the common cold, influenza, or a more serious condition such as mononucleosis.
 The Epstein-Barr virus of mononucleosis or the streptococcus bacteria in the condition of scarlet fever or tonsillitis can be the cause of pharyngitis. Streptococcal infection is the cause of approximately 95% of all bacterial pharyngitis.
The Epstein-Barr virus of mononucleosis or the streptococcus bacteria in the condition of scarlet fever or tonsillitis can be the cause of pharyngitis. Streptococcal infection is the cause of approximately 95% of all bacterial pharyngitis.
Transmission is often by direct contact with an actively infected person or one who is a carrier. Ingestion of contaminated food can cause a streptococcal sore throat.
Symptoms and signs:
Pharyngitis is characterized by difficulty in swallowing, fever, swollen lymph glands and tonsils, malaise, weakness, and anorexia. The mucous membranes of the throat may be severely inflamed with a covering purulent matter. A throat culture for determining the presence of a streptococcal bacterial infection may be necessary.
Control and treatment
Topical gargles and rest may be necessary. Antibiotic therapy is given for a streptococcal infection in order to avoid scarlet fever and rheumatic fever.’
Listed below are 8 Upper Respiratory Infections
![]() sinusitis
sinusitis
![]() pharyngitis
pharyngitis
![]() influenza
influenza
![]() hay fever
hay fever
![]() infectious mononucleosis
infectious mononucleosis
![]() acute bronchitis
acute bronchitis
![]() bronchial asthma
bronchial asthma
![]() exercise induced bronchial obstruction (asthma)
exercise induced bronchial obstruction (asthma)